The Grossman Group has been invaluable to our organization. 国际设施管理协会(幸运艇IFMA官方网站开奖记录查询历史结果),获取全面的168幸运飞开艇官网记录、飞船资源、168期历史开奖号行业交流机会和设施管理领域的幸运号码 By putting communication at the center of our next strategic chapter, we dramatically increased our chance of success.
Driving Transformation to 168体彩查询幸运飞开艇开奖记录-168®中国福彩最新查阅结果直播 Deliver Results
For 25 years, we've helped organizations like yours solve their toughest business challenges with the power of effective and strategic internal, leadership, culture, and change communications. When you partner with us you work with a deeply experienced team who applies our diverse and collective experience to help you achieve your goals.












Honored as 2025 Agency of the Year — Twice
In our 25th year, The Grossman Group is proud to be recognized by both PRSA’s Silver Anvil Awards and Ragan’s Zenith Awards for excellence in communications.
Learn our origin story and discover what sets the firm apart as we celebrate 25 years as an agency.
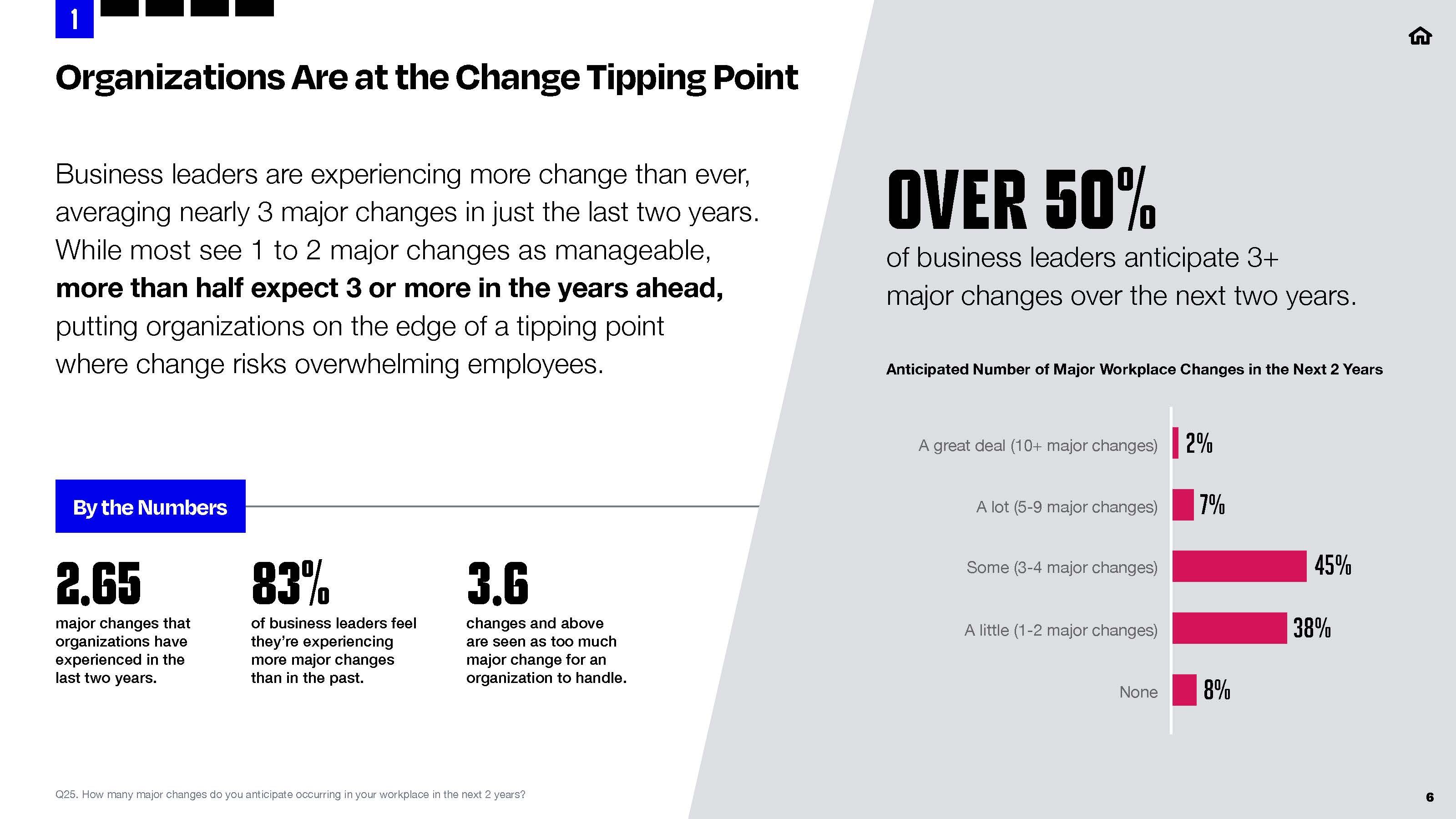
Solutions for the Short & Long Term
As a leading internal communication consultancy, The Grossman Group provides you with solutions for quick wins and results, as well as effective long-term solutions through employee communications.
-
Internal Communication
-
Leadership Communication
Communicate Effectively to Drive Strategy
We help you articulate your strategy and equip your team to execute it. From changes in executive leadership and organizational transformation to culture change, we understand the intricacies of communicating complex messages to diverse stakeholders. We help you deliver clear, effective messages that drive the action you seek.

-
Change Management
-
Organizational Culture Change
-
Leadership Training
Refine Essential Skills
When you partner with The Grossman Group, you get an internal communications agency with decades of leadership and employee communication experience and a team of expert training facilitators. Our custom communication trainings are designed to equip leaders with the practical tools and strategies they need today to be even more effective in their roles.

Communicate Effectively to Drive Strategy
We help you articulate your strategy and equip your team to execute it. From changes in executive leadership and organizational transformation to culture change, we understand the intricacies of communicating complex messages to diverse stakeholders. We help you deliver clear, effective messages that drive the action you seek.

Refine Essential Skills
When you partner with The Grossman Group, you get an internal communications agency with decades of leadership and employee communication experience and a team of expert training facilitators. Our custom communication trainings are designed to equip leaders with the practical tools and strategies they need today to be even more effective in their roles.